As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly prevalent, their safety features are evolving rapidly. These advancements are not just about protecting passengers in the event of a crash, but also about preventing accidents from happening in the first place.
This
blog will explore the cutting-edge technologies in EV crash prevention and
response, highlighting how these innovations are making our roads safer and
featuring examples from leading EV brands.
Introduction to EV Safety
Electric
vehicles have garnered significant attention for their environmental benefits,
but safety is equally paramount. Manufacturers are investing heavily in
research and development to enhance both crash prevention and response
mechanisms.
Crash Prevention Technologies
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
(ADAS)
One
of the most significant advancements in EV safety is the integration of
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). These systems use a combination of
sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to monitor the vehicle's
surroundings and assist the driver in avoiding potential hazards.
Features of ADAS
Automatic
Emergency Braking (AEB): Detects imminent collisions and applies the brakes to
prevent or mitigate the impact.
Example: Tesla's Model 3 and
Model Y come equipped with AEB as a standard feature.
Example: Nissan Leaf includes
LDW as part of its ProPILOT Assist system.
Example: Audi e-tron features
ACC to enhance highway driving safety.
Impact on Safety
ADAS
significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents caused by human error.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ADAS
features can prevent up to 20% of crashes.
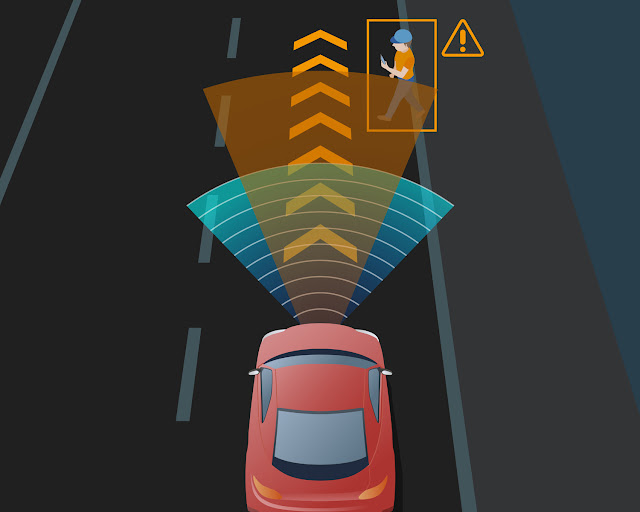
Collision Avoidance Systems
EVs
are increasingly equipped with collision avoidance systems that use radar,
lidar, and cameras to detect obstacles and pedestrians.
Key Technologies
Forward
Collision Warning (FCW): Warns the driver of an impending collision with a vehicle
or object in its path.
Example: Hyundai Kona
Electric is equipped with FCW as part of its safety suite.
Example: The Volvo XC40
Recharge includes pedestrian detection to enhance urban safety.
Enhanced Sensor Technologies
Modern
EVs utilize a suite of advanced sensors that provide real-time data to onboard
safety systems. These sensors enhance the vehicle's ability to detect and
respond to potential hazards.
Ultrasonic
Sensors:
Detect objects close to the vehicle, aiding in parking and low-speed maneuvers.
Example: BMW i3 uses
ultrasonic sensors for its parking assistance system.
Infrared
Cameras:
Improve visibility in low-light conditions and detect heat signatures from
pedestrians and animals.
Example: The Jaguar I-PACE
uses infrared cameras to enhance night driving safety.
Crash Response Innovations
Battery Safety
A
critical aspect of EV safety is managing the battery during and after a crash.
Lithium-ion batteries, while powerful, can pose risks if damaged.
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
BMS
are crucial for monitoring battery health and managing performance. They help
prevent overheating and short circuits, which are critical during a crash.
Example: Chevrolet Bolt EV
features a robust BMS to ensure battery safety.
The
design and materials used in EVs are optimized for safety. Manufacturers employ
advanced engineering techniques to ensure the vehicle's structure can absorb
and dissipate crash forces effectively.
Crumple Zones
Crumple
zones in EVs are designed to absorb impact energy, reducing the force
transmitted to occupants.
Example: Tesla Cybertruck
features advanced crumple zones to enhance passenger safety.
Using
high-strength steel and aluminum alloys enhances the structural integrity of
EVs, providing better protection during a crash.
Example: Rivian R1T utilizes
high-strength materials in its chassis for superior crash protection.
Post-Crash Safety Features
EVs
are equipped with features that activate after a crash to protect occupants and
facilitate rescue efforts.
Automatic Emergency Call (eCall)
In
the event of a crash, eCall systems automatically contact emergency services,
providing the vehicle's location and other critical information.
Example: Mercedes-Benz EQC
includes eCall functionality for enhanced post-crash response.
To
prevent electrical hazards, EVs are designed to isolate the battery in the
event of a crash, cutting off the power supply to prevent fires and electric
shock.
Example: Nissan Leaf features
battery isolation technology to enhance post-crash safety.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Global Safety Standards
Various
international bodies have established safety standards for EVs to ensure they
meet stringent safety criteria.
Euro NCAP
The
European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) tests and rates the safety of
vehicles, including EVs, based on crash performance and safety features.
Example: The Audi e-tron has
received high safety ratings from Euro NCAP.
The
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States
sets regulations for vehicle safety, including crash testing and performance
standards for EVs.
Example: The Tesla Model 3
has achieved high safety ratings from NHTSA.
Industry Best Practices
Manufacturers
are adopting best practices to enhance the safety of their EVs, focusing on
both preventative measures and post-crash response.
Collaborative Efforts
Automakers
are working together and with technology companies to share data and improve
safety systems continuously.
Future Directions in EV Safety
Autonomous Driving
The
development of autonomous driving technology promises to further enhance EV
safety by reducing the potential for human error.
Example: Waymo, Google’s
autonomous vehicle project, is pioneering self-driving technology in electric
vehicles.
V2X
communication allows EVs to interact with other vehicles, infrastructure, and
even pedestrians, creating a more connected and safer driving environment.
Example: The Nissan Ariya
includes V2X technology to enhance safety and efficiency.
Read:Top 5 AI Innovations Transforming the Automotive Industry











Comments
Post a Comment